Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
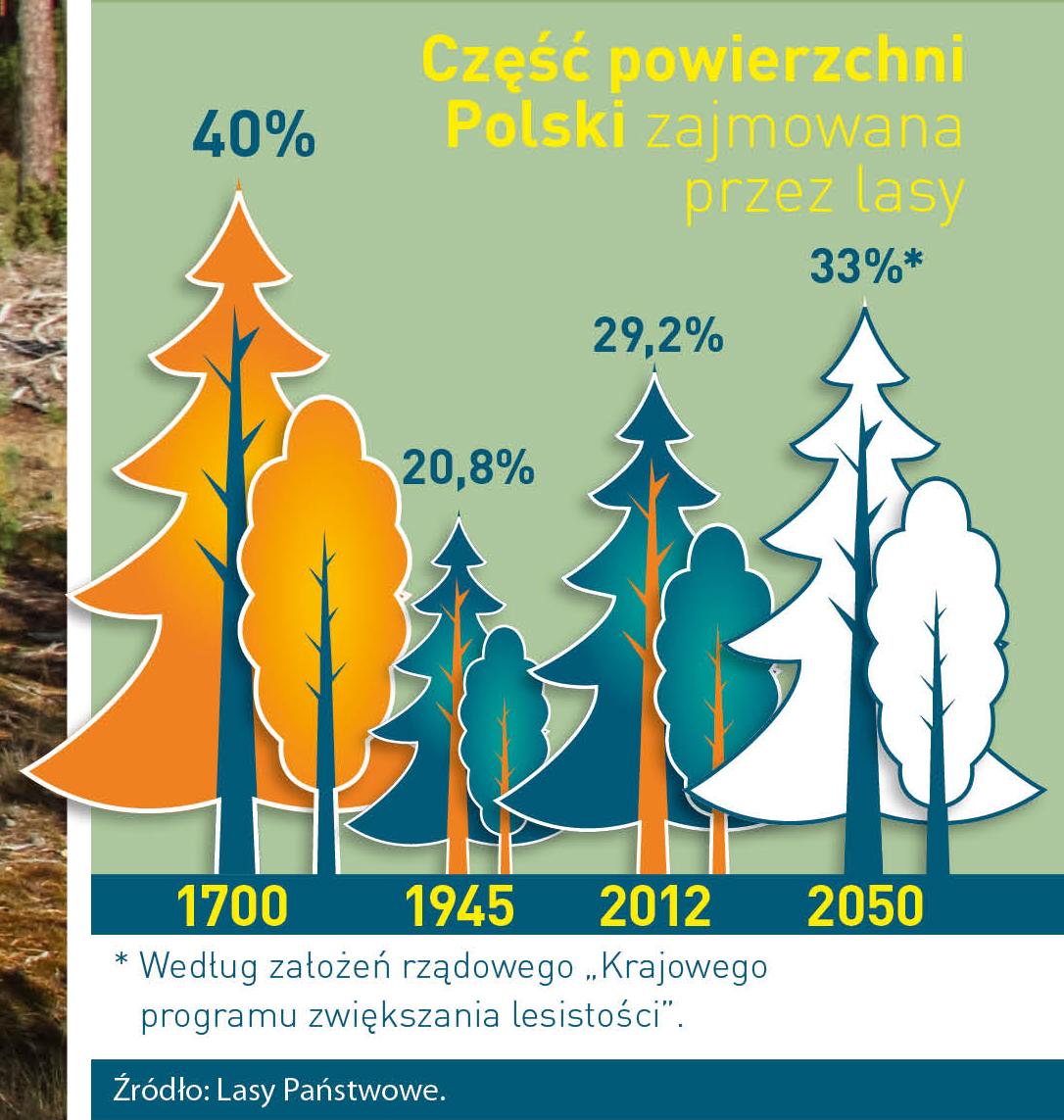
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Lasy nadleśnictwa
Lasy nadleśnictwa
Ogólna powierzchnia Nadleśnictwa wynosi wg stanu na 29.10.2024 r. 17915 ha, w tym powierzchnia leśna 17 153 ha.
Nadleśnictwo zostało podzielone na 12 leśnictw, przeciętna powierzchnia leśnictwa wynosi 1492,91 ha.
Charakterystyka przyrodniczo-leśna
Nadleśnictwo leży w Bałtyckiej krainie przyrodniczo-leśnej, dzielnicy Pobrzeża Słowińskiego, mezoregionie Równiny Białogardzkiej. Rzeźba terenu ukształtowana w czasie ostatniego zlodowacenia jest zróżnicowana, przechodzi od terenu równinnego do pagórkowatego. Wysokość nad poziom morza waha się od 30 m do 130 m. Stosunkowo długi okres wegetacyjny, duży opad, ciepłe lata i łagodne zimy sprzyjają produkcji leśnej. W związku z bliskością Bałtyku obserwuje się jego łagodny wpływ na klimat. Przeciętna temperatura roczna wynosi około 7 o C, przy rocznym opadzie około 790 mm. Okres wegetacyjny trwa średnio 240 dni. Niekorzystny wpływ późnych przymrozków często odbija się na jakości upraw. Obszar Nadleśnictwa pokrywają w przeważającej części piaski sandrowe z płatami piasków zwałowych i glin zwałowych. Wzdłuż cieków i zbiorników wodnych występują współczesne osady bagienne: torfy i mursze. Przeważającym typem gleby są gleby rdzawe zajmujące 71 % powierzchni. Ponadto występują gleby bielicowe 12 %, brunatne 4 % i gleby torfowo - murszowe 4 %.
Procentowy udział typów siedliskowych lasu
Dominującymi typami siedliskowymi są bory świeże, bory mieszane świeże i lasy mieszane świeże. Łącznie siedliska borowe zajmują 80 %, a lasowe 20 % powierzchni. Najliczniej występującym gatunkiem lasotwórczym jest sosna, zajmująca 84 % gruntów zalesionych, tworząca drzewostany jednogatunkowe, a na siedliskach żyźniejszych mieszane ze świerkiem, dębem, bukiem i brzozą. Udział gruntów porolnych wynosi około 50%. Drzewostany te są często lukowate i opanowane przez hubę korzeniową. Drugim gatunkiem co do powierzchni jest świerk - 5 %. Z cenniejszych gatunków występują buk 3 %, dąb 2 %, modrzew 1 % gruntów zalesionych.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański